The Sweet World of Sweets: Between Pleasure and Caution
In the gourmet kingdom of candy, sweet temptation attracts as much as it questions. From traditional hard caramel to tangy jellies and irresistible marshmallow bears, each candy is a little explosion of flavors to delight our taste buds. But behind this delicious façade lie important questions about their impact on health, their manufacture, and possible alternatives. In this article, we delve into the sweet world of candy to explore all its aspects, from health effects to responsible consumption choices.
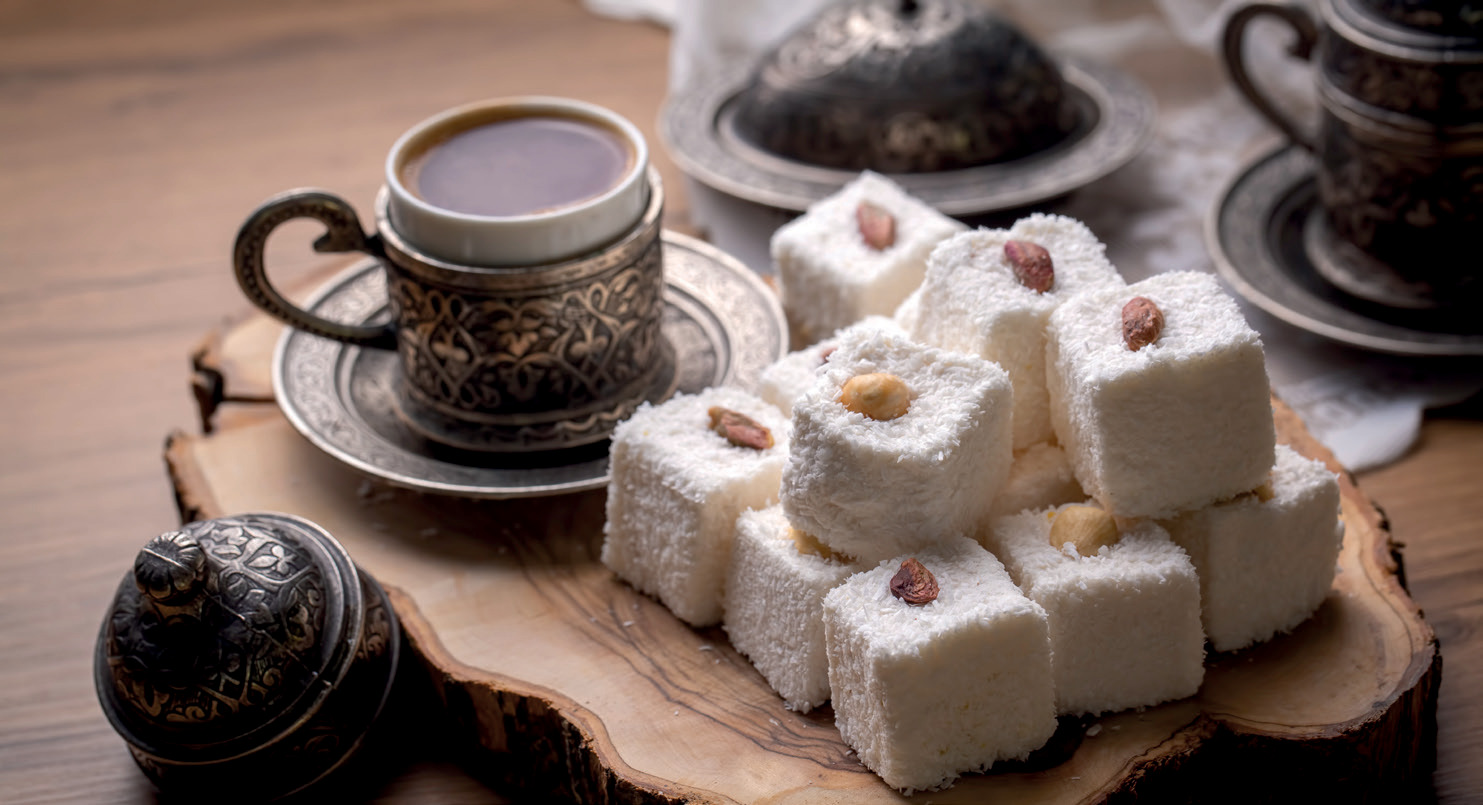

The cradle of confectionery
Candies, those delicious sweet treats that delight young and old alike, have a fascinating history that goes back centuries. From simple sugar cubes to the colored and flavored candies we know today, their evolution has been marked by human ingenuity and technological advances. In this article, we delve into the sweet history of sweets, exploring their origins, transformations and place in global culture.
Ancient origins:
The origins of sweets go back to ancient times, when the Egyptians and Greeks used honey and fruit to prepare sweet treats. The Romans, meanwhile, were famous for their honey and sugar confectionery. However, these sweets were reserved for the rich and were not available to everyone.
A turning point in the Middle Ages:
In the Middle Ages, the art of confectionery began to develop in Europe, and sweets became increasingly popular. Monks were often responsible for preparing these sweets, making them from honey, fruit and spices. Sweets were used for medicinal purposes, supposedly with curative properties.
The arrival of sugar:
The history of sweets was transformed by the arrival of sugar in Europe in the 16th century. Sugar was initially considered a luxury product and was reserved for the aristocracy. Sweets have become symbols of wealth and social status. Confectioners began experimenting with new recipes and techniques to create more varied and refined sweets.
The Industrial Revolution:
The Industrial Revolution of the 19th century played a key role in the evolution of the candy industry. Technological advances have enabled the mass production of sweets, making them more accessible to a wider public. The first candy factories were created, and innovations such as steam engines and candy presses revolutionized manufacturing.
The emergence of modern sweets:
In the 20th century, candy continued to evolve with the introduction of new ingredients, flavors and shapes. Gummy candies, such as gummy bears, made their appearance, quickly becoming popular. Iconic brands such as Haribo were created, launching iconic sweets that are still enjoyed today.
Sweets in popular culture:
Sweets have acquired an important place in popular culture, becoming symbols of fun and childhood. Iconic sweets such as lollipops, dragées and chocolate bars have become recognizable icons the world over. Sweets are often associated with moments of celebration, parties and sharing.
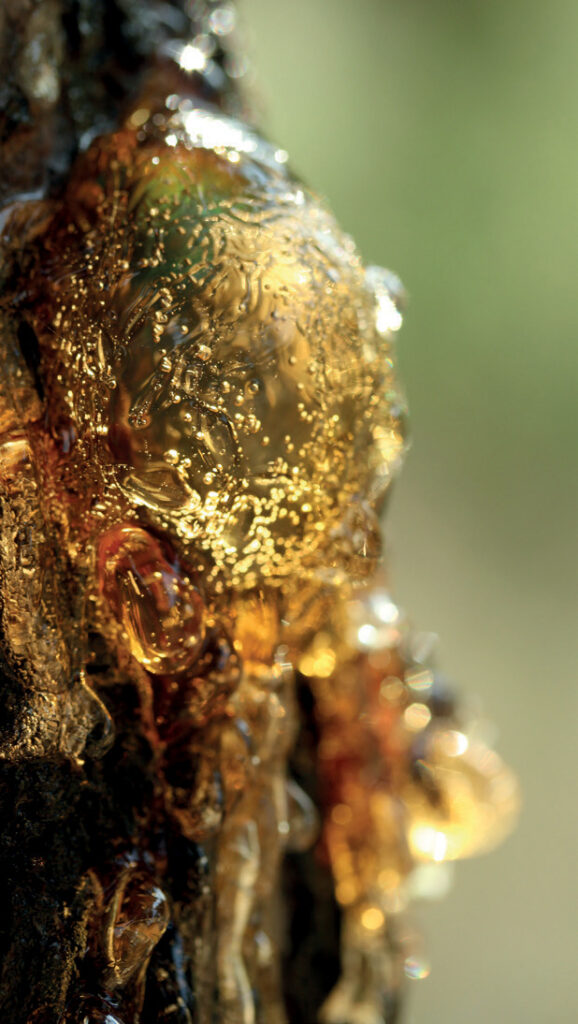

The ancient origins of chewing gum
Chewing gum has become a popular treat in many cultures around the world. Whether for breath freshening, relaxation or simply for the pleasure of chewing, chewing gum has a rich and interesting history. In this article, we delve into the history of chewing gum, from its ancient origins to its worldwide popularity today.
Ancient origins:
The history of chewing gum goes back thousands of years. The earliest evidence of chewing dates back to the ancient civilization of the Mesopotamians, who chewed tree resin to clean their teeth and refresh their breath. The ancient Greeks and Romans also used natural resins and chewing gums for the same reasons.
Native customs in the Americas:
The indigenous peoples of the Americas had their own chewing customs long before the arrival of Europeans. The Mayans and Aztecs chewed sap from the sapodilla, a tropical tree, to extract the latex and obtain a kind of chewing gum. These practices spread and were observed by the first European explorers.
The rise of modern chewing gum:
Modern chewing gum as we know it today began to take shape in the 19th century. In 1848, John B. Curtis developed and marketed the first chewing gum in the United States. This chewing gum was made from spruce sap, which gave it a resinous flavor. However, chewing gum wasn’t very popular back then.
The chicle revolution in chewing gum:
The rise of chewing gum came about when Thomas Adams, an American businessman, discovered chicle, a sap from the chicle tree in Central America. He realized that chicle had commercial potential as a base for chewing gum. In 1871, Adams launched the first chicle-based chewing gum, and it quickly gained in popularity.
The era of modernization and diversification:
In the early 20th century, many chewing gum brands emerged, using different flavors, ingredients and attractive packaging to attract consumers. Brands such as Wrigley’s and Dubble Bubble have become emblematic of the chewing gum industry. New technological advances have also improved the texture, shelf life and flavor of chewing gum.
Chewing gum in popular culture:
Chewing gum has become a staple of popular culture. He has been associated with famous characters such as Bazooka Joe and has appeared in films, songs and commercials. What’s more, chewing gum has been recognized for its beneficial effects on concentration, stress reduction and mood enhancement.
The history of chewing gum is proof of the evolution of consumer habits and tastes over the centuries. From its humble beginnings in ancient chewing practices to modern chewing gums available in a variety of flavors and shapes, chewing gum has come a long way. Whether for the pleasure of chewing or for its refreshing benefits, chewing gum has become a daily companion for many people around the world.
Sugar and the brain
Sugar-rich foods, via sensors in the mouth but also in the intestine, trigger the release of dopamine in the brain: a sensation of pleasure, reward and excitement. But dopamine also interacts with other neurotransmitters and brain systems to create complex effects on behavior and emotions. Researchers interested in food addiction are trying to understand the complex mechanisms that lead our bodies to develop a dependency on certain foods. Studies are focusing on the potential roles of dopamine, opiate receptors, the gut and the hypothalamus in regulating our food preferences and behaviors.

What are the health effects of sweets?
Sweets, with their high sugar content, can have a number of health effects if consumed in excess. Regular candy consumption can contribute to weight gain, oral health problems such as cavities and tooth erosion, and fluctuations in blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. What’s more, some sweets contain additives such as artificial colorings or preservatives that may be associated with long-term health problems.
What’s the difference between hard candies and jelly beans?
The main difference between hard and jelly candies lies in their texture and manufacturing method. Hard candies are generally made by melting sugar with other ingredients, then cooling it to obtain a solid, crunchy texture. Jelly candies, on the other hand, are made by mixing sugar with gelatin or other gelling agents, then allowing them to harden into a chewy, soft texture.
How are sweets made?
Candy-making is a complex process that varies according to the type of candy. Sugar is usually heated to a high temperature until it melts, then other ingredients such as flavoring, coloring and gelling agents are added. The mixture is then poured into molds and cooled until hardened. Once hardened, the candy is removed from the mould, packaged and ready to eat.
Are sugar-free sweets better for your health?
Sugar-free candy may seem like a healthier alternative, but it’s not without its drawbacks. Although they contain less sugar, they can still have an impact on oral health due to their artificial sweetener content, which can also cause gastrointestinal problems in some people. What’s more, sugar-free candies can sometimes have a different taste and a less satisfying texture than their sugary counterparts.
The world’s most popular types of candy
In the vast world of sweets, a few varieties stand out for their worldwide popularity. Gummy candies, such as gummy bears and gummy worms, are appreciated for their chewy texture and varied flavors. Hard candies, such as lollipops and sour candies, are also popular for their long shelf life and ease of transport. Last but not least, chocolate bonbons, whether caramel or hazelnut-filled, remain a must-have for many sweet tooths around the world.
How can I avoid eating too many sweets?
For those who want to limit their candy intake, a few simple strategies can help. Limiting access to sweets by not keeping them on hand, opting for healthier alternatives like fresh fruit or low-sugar snacks, and practicing moderation by enjoying sweets sparingly can all help reduce temptation and maintain a balanced diet.
Sweets and tooth decay
Yes, excessive consumption of sweets, especially those containing sugar, can increase the risk of dental caries. When sugar is consumed, bacteria in the mouth feed on it, producing acids that attack tooth enamel. Over time, this can lead to cavities and other dental problems. However, by practicing good oral hygiene, brushing regularly and limiting the consumption of sugary sweets, it is possible to reduce this risk.
Candy shelf life
The shelf life of candy varies according to the type and ingredients used in its manufacture. In general, hard candies have a longer shelf life than jelly beans due to their low moisture content. However, sweets can start to lose their freshness and flavor over time, so we recommend consuming them within the time indicated on the packaging for the best taste experience.
Healthy alternatives to traditional sweets
For those looking for healthier alternatives to traditional sweets, there are several options to explore. Fresh fruit, such as berries, apple slices or orange segments, offer a natural, nutritious alternative to sugary sweets. What’s more, nut- or seed-based snacks, such as roasted almonds or pumpkin seeds, can satisfy crunchy, salty cravings without the drawbacks of added sugar.
The effects of colorants and additives in sweets
The colorants and additives found in sweets can have various effects on health. Some artificial colors have been associated with behavioral problems in children, while other additives, such as artificial sweeteners, can cause gastrointestinal problems in some sensitive individuals. That’s why we recommend reading candy labels carefully, and opting for products made with natural ingredients whenever possible.
Sweets can be a delicious indulgence to enjoy from time to time, but it’s important to consume them in moderation and make informed choices when it comes to your health. By exploring the different types of candy, understanding their impact on health and opting for healthier alternatives where possible, everyone can enjoy the sweet world of candy while taking care of their well-being.